How to operate a drone is a question many ask, and this guide provides a comprehensive answer. From understanding basic components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced flight techniques and adhering to regulations, we’ll explore every aspect of safe and effective drone operation. This journey will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly, capturing stunning aerial footage and exploring the exciting world of drone technology.
We’ll cover everything from the fundamentals of drone mechanics and flight controls to the intricacies of camera operation, image composition, and legal considerations. We’ll also delve into essential maintenance practices and troubleshooting tips to ensure the longevity of your drone. By the end, you’ll have a solid understanding of how to operate a drone safely and effectively, regardless of your skill level.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the various components of a drone and their functions is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section provides a detailed overview of key drone parts and a glossary of commonly used terms.
Drone Component Functions

A drone’s functionality relies on the coordinated operation of several key components. Let’s explore each one.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of regulations and safe flying practices. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone and improve your skills. Ultimately, responsible operation ensures both safety and enjoyment in the exciting world of drone technology.
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, enabling the drone to take off, fly, and maneuver. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers. Brushless motors are commonly used in modern drones for their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, the flight controller is a small computer that processes sensor data and controls the motors to maintain stability and execute flight commands. It integrates data from various sensors, such as gyroscopes, accelerometers, and barometers.
- Battery: The power source for the drone, typically a Lithium Polymer (LiPo) battery. Battery capacity directly impacts flight time.
- GPS Module: This component receives signals from GPS satellites, enabling precise positioning and navigation. Essential for features like waypoint navigation and return-to-home.
- Radio Transmitter/Receiver: This system allows the pilot to control the drone wirelessly. The transmitter sends commands, and the receiver on the drone interprets and executes them.
- Camera: Many drones are equipped with cameras for capturing aerial photos and videos. Camera features vary widely, including resolution, image stabilization, and field of view.
- Gimbal (Optional): A stabilized mount for the camera, reducing vibrations and improving image quality.
Drone Terminology Glossary
Here’s a glossary of common terms used in drone operation.
- Altitude Hold: A flight mode that maintains a constant altitude.
- Gimbal Lock: A condition where the gimbal loses its ability to rotate freely in one or more axes.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): An automated function that guides the drone back to its starting point.
- Failsafe: A safety mechanism that takes over control of the drone in case of signal loss or other malfunctions.
- Waypoint: A pre-programmed location that the drone will fly to.
- ESC (Electronic Speed Controller): Regulates the speed of each motor.
- mAh (milliampere-hour): A unit of battery capacity.
- LiPo (Lithium Polymer): A type of rechargeable battery commonly used in drones.
Drone Battery Comparison
Different battery types offer varying performance characteristics. The table below compares LiPo and LiFePO4 batteries.
| Battery Type | Capacity (mAh) | Voltage (V) | Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo | 1500-5000+ | 11.1-22.2 | Variable depending on capacity |
| LiFePO4 | 1000-3000 | 12.8 | Generally heavier than LiPo for same capacity |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for safe drone operation. Ignoring this step can lead to accidents and equipment damage.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to check out for comprehensive guidance is this helpful guide on how to operate a drone. From there, practice is key to mastering the skills needed for safe and effective drone operation.
Remember always to prioritize safety and responsible flying practices.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, perform the following checks:
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage.
- Ensure the battery is fully charged and properly connected.
- Check the GPS signal strength and satellite lock.
- Verify that all propellers are securely attached.
- Review the weather conditions and ensure they are suitable for flight.
- Check the drone’s firmware is up-to-date.
- Familiarize yourself with the local airspace regulations.
- Confirm that you have the necessary permissions or licenses for drone operation in the chosen location.
- Have a designated spotter or assistant present during flights.
Emergency Procedures
In case of malfunctions or loss of control, immediate action is critical.
- Loss of Signal: Most drones have a Return-to-Home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately if signal is lost.
- Malfunction: Attempt to regain control using the emergency controls (if available). If unable to regain control, prepare for a controlled crash, aiming for a soft landing in a safe area.
- Battery Failure: If the battery fails, initiate RTH immediately, or perform a controlled descent.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Flowchart
The following flowchart illustrates the steps for a safe takeoff and landing.
(A textual representation of a flowchart is difficult to provide in HTML. A visual flowchart would be more effective here. The flowchart would depict steps like: Pre-flight checks -> Power on drone and controller -> Calibrate GPS -> Check for obstructions -> Initiate takeoff -> Hover and check stability -> Fly -> Initiate landing -> Power off drone and controller.)
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers

Understanding basic flight controls is fundamental to safe and competent drone operation. This section details the fundamental controls and maneuvers.
Basic Flight Controls
Most drones use a four-channel control system:
- Throttle: Controls the drone’s altitude. Increasing throttle makes it ascend, decreasing throttle causes it to descend.
- Pitch: Controls movement forward and backward. Tilting the control stick forward moves the drone forward; tilting it backward moves it backward.
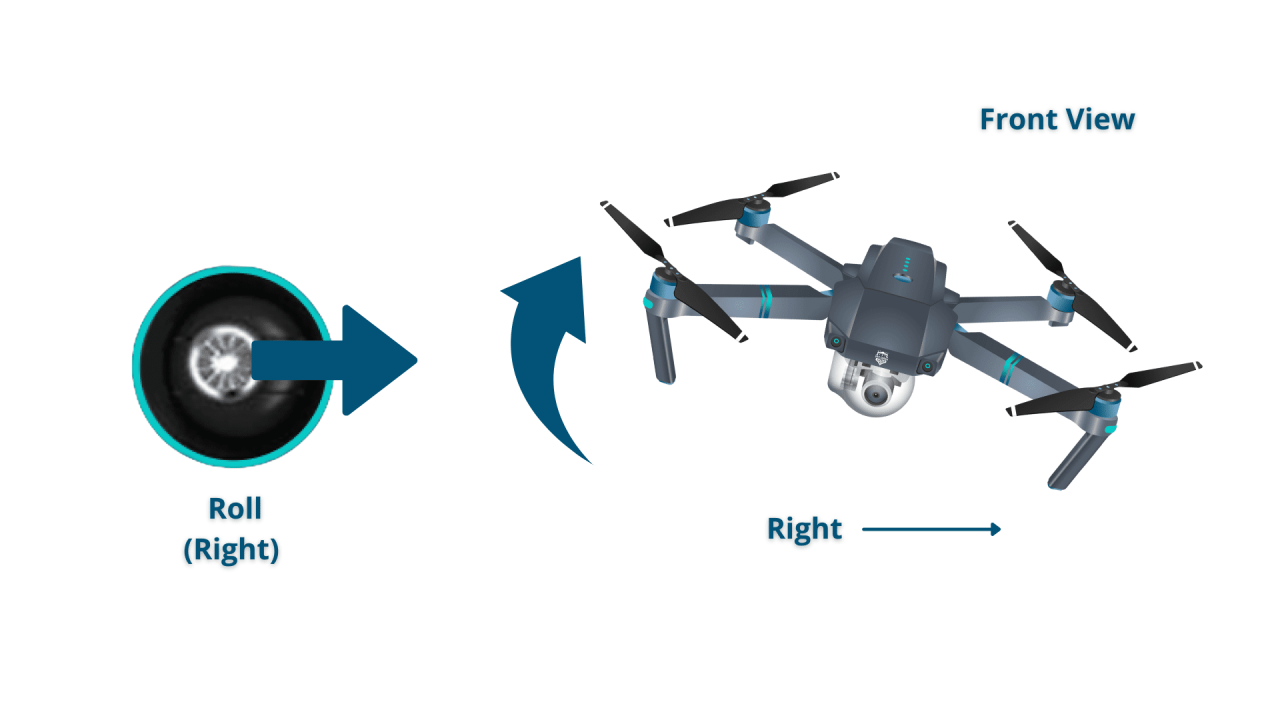
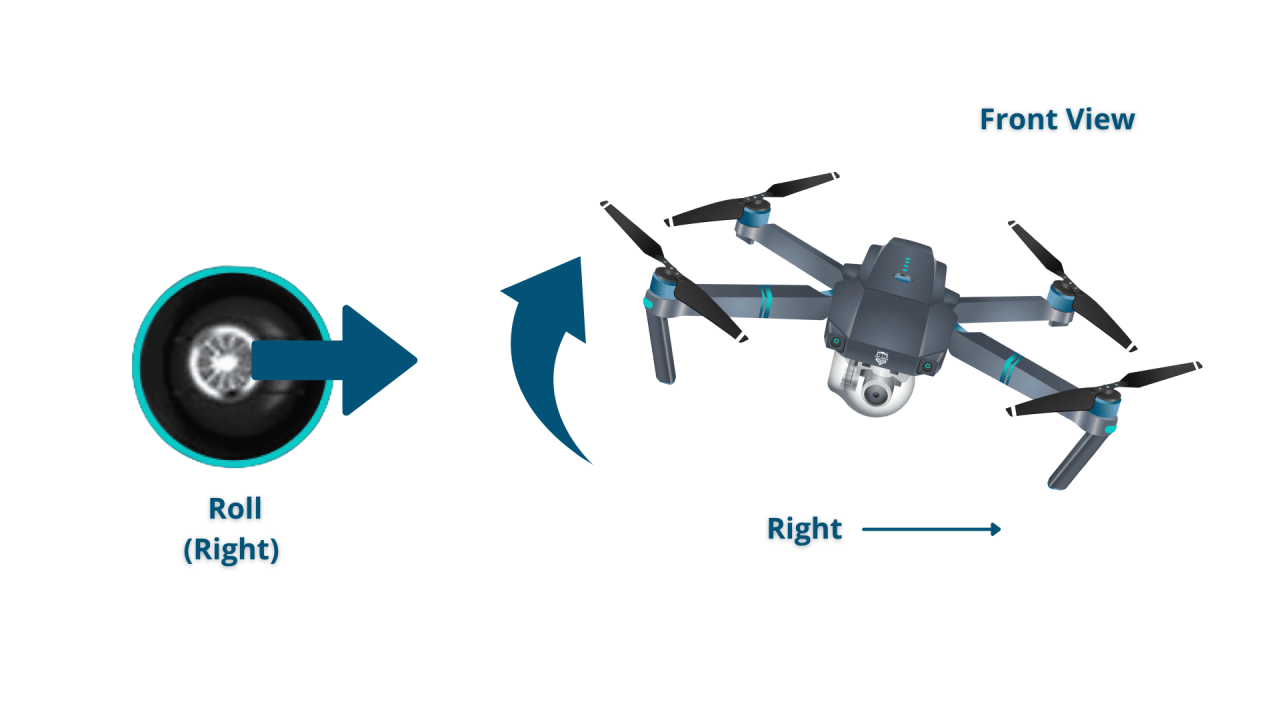
- Roll: Controls movement left and right. Tilting the control stick left moves the drone left; tilting it right moves the drone right.
- Yaw: Controls rotation around the vertical axis (turning left or right).
Basic Flight Maneuvers
Practice these maneuvers in a safe, open area away from obstacles:
- Hovering: Maintaining a stable position in the air. Requires precise control of throttle and minor adjustments to pitch, roll, and yaw.
- Ascending/Descending: Controlled vertical movement using the throttle control.
- Turning: Rotating the drone left or right using the yaw control.
- Forward/Backward/Sideways Movement: Using the pitch and roll controls to move the drone in the desired direction.
Achieving Smooth and Controlled Flight
Smooth flight requires practice and finesse. Avoid abrupt movements and use gentle, controlled inputs to the control sticks. Focus on maintaining a stable hover before attempting more advanced maneuvers.
Navigation and GPS Usage
Effective navigation is crucial for safe and efficient drone operation. This section details the use of GPS for navigation and waypoint planning, along with troubleshooting common issues.
GPS Navigation and Waypoint Planning, How to operate a drone
Many drones utilize GPS for precise positioning and autonomous flight. Waypoint planning allows you to pre-program a flight path, enabling the drone to follow a series of defined points.
- Setting Waypoints: Most drone apps allow you to create waypoints by tapping locations on a map.
- Following Waypoints: Once waypoints are set, the drone will autonomously follow the defined path.
- Adjusting Waypoints: You can modify or delete waypoints during the planning process or even during flight (depending on the drone and app).
GPS Signal Strength and Interference
GPS signal strength is affected by several factors, including obstructions (buildings, trees), atmospheric conditions, and interference from other electronic devices.
- Obstructions: Fly in open areas with clear views of the sky for optimal GPS signal.
- Atmospheric Conditions: Heavy cloud cover or rain can weaken the signal.
- Interference: Avoid flying near sources of radio frequency interference.
Common GPS-Related Issues and Troubleshooting
Here are some common GPS problems and their solutions:
- Weak Signal: Relocate to an area with better GPS reception.
- No Satellite Lock: Ensure the drone has a clear view of the sky and wait for the GPS to acquire a lock.
- GPS Drift: This can be caused by interference or poor signal. Try to find a location with better reception.
Drone Camera Operation and Image/Video Capture
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding your drone’s camera settings and features. This section explores camera operation and image/video capture techniques.
Drone Camera Settings and Features
Drone cameras offer various settings to control image and video quality:
- Resolution: Choose the appropriate resolution based on your needs (e.g., 4K, 1080p).
- Frame Rate: The number of frames per second (fps) affects the smoothness of video. Higher fps results in smoother video but requires more storage space.
- ISO: Controls the camera’s sensitivity to light. Lower ISO is generally better for sharpness, while higher ISO is needed in low-light conditions.
- Shutter Speed: Controls how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. Adjust this to avoid motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the camera. A wider aperture (lower f-stop number) allows more light.
- White Balance: Adjusts the color temperature to ensure accurate colors.
Capturing High-Quality Images and Videos
To capture professional-looking aerial footage, consider these tips:
- Steady Shots: Use a gimbal for smoother footage and avoid jerky movements.
- Lighting: Shoot during the golden hour (sunrise and sunset) for optimal lighting.
- Composition: Apply the rule of thirds and other composition techniques to create visually appealing images.
- Storage: Use high-capacity SD cards to avoid running out of storage space.
Different Camera Modes and Their Applications
Drone cameras offer various modes:
- Photo Mode: For capturing still images.
- Video Mode: For recording video footage.
- Timelapse Mode: For creating time-lapse videos.
- Panorama Mode: For capturing wide panoramic images.
Drone Laws and Regulations
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to local laws and regulations. This section provides a general overview; always check your specific region’s rules.
Overview of Drone Laws and Regulations
Drone laws vary by country and region. Common regulations include restrictions on airspace, registration requirements, and limitations on flight altitude and distance.
Restricted Airspace and No-Fly Zones
Many areas have restricted airspace, including airports, military bases, and national parks. Check with your local aviation authority for a complete list of restricted areas.
Best Practices for Complying with Drone Regulations
To ensure legal and safe drone operation:
- Register your drone if required.
- Always check for restricted airspace before flying.
- Maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Respect the privacy of others.
- Fly responsibly and avoid endangering others.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting: How To Operate A Drone
Regular maintenance is crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and preventing malfunctions. This section details a maintenance schedule and common troubleshooting steps.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
Follow this schedule for optimal drone performance:
- After Each Flight: Inspect for damage, clean propellers and body.
- Weekly: Check battery health, inspect motor mounts and screws.
- Monthly: Thoroughly inspect all components, clean the camera lens.
- Quarterly: Calibrate the sensors and update firmware.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Here are some common issues and their solutions:
- Propeller Damage: Replace damaged propellers.
- Battery Issues: Check battery health, charge properly, or replace if necessary.
- GPS Problems: Ensure clear GPS signal, recalibrate if needed.
- Motor Problems: Inspect motors for damage, replace if faulty.
- Flight Controller Issues: May require professional repair or replacement.
Essential Tools and Spare Parts for Drone Maintenance
Keep these items on hand for maintenance:
- Propeller wrench
- Screwdrivers (various sizes)
- Spare propellers
- Cleaning cloth
- Battery charger
- Spare batteries
Advanced Flight Techniques
Once you’ve mastered the basics, you can explore more advanced flight techniques. This section explores advanced maneuvers and different flight controllers.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Advanced techniques require significant practice and skill:
- Precision Hovering: Maintaining a perfectly stable hover in challenging conditions.
- Advanced Maneuvers: This includes flips, rolls, and other acrobatic movements.
- Low-Altitude Flight: Requires precise control and awareness of surroundings.
Use of Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of stability and control:
- Sport Mode: Offers increased responsiveness and speed.
- Cine Mode: Prioritizes smooth, cinematic movements.
- Beginner Mode: Limits speed and responsiveness for easier control.
Comparison of Flight Controllers
Different flight controllers offer varying features and capabilities. Some are more advanced, offering features like obstacle avoidance and autonomous flight modes.
Drone Photography and Videography Composition
Creating aesthetically pleasing aerial shots requires understanding composition techniques and utilizing environmental factors to your advantage.
Tips and Techniques for Achieving Aesthetically Pleasing Drone Shots
Employ these techniques to elevate your aerial photography and videography:
- Rule of Thirds: Place key elements along imaginary lines that divide the frame into thirds.
- Leading Lines: Use lines within the scene to guide the viewer’s eye.
- Symmetry and Patterns: Capture scenes with repeating patterns or symmetrical elements.
- Framing: Use natural elements, like trees or buildings, to frame your subject.
Rules of Composition in Aerial Photography and Videography
Applying fundamental composition principles enhances the visual impact of your aerial work.
Using Lighting and Weather Conditions to Your Advantage
Leverage natural lighting and weather to enhance your shots. Golden hour lighting produces warm, aesthetically pleasing images, while overcast days offer soft, diffused light.
Mastering drone operation is a rewarding experience that opens up a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to innovative applications across various industries. Remember, responsible operation is paramount, so always prioritize safety, adhere to regulations, and continuously refine your skills. With practice and a commitment to safe flying, you’ll confidently navigate the skies and unlock the full potential of your drone.
Enjoy the flight!
FAQ Section
What is the best type of drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and automated features are ideal for beginners. Research models known for their stability and ease of use.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration is crucial for accurate flight. Calibrate before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any significant impacts.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
Immediately switch to a lower altitude and attempt to regain signal. If unsuccessful, perform a controlled emergency landing.
How do I store my drone batteries safely?
Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from flammable materials, and at approximately 50% charge to prolong their lifespan.